In this diagram which events out of A B C and D occur at the same time. On the rotated grid we draw the spacetime diagram of Alice and two such mirrors one to the right the direction in which Alice faces and the other to the left.
In Figure 7 we mark two events A and B located at the same point in space but different points in time in the.
. The parallelogram OMTN represents one tick of Alices longitudinal light clock where the spatial trajectories of the light signals are parallel to the direction of relative motion. The star goes supernova at space-time point S. A spacetime diagram or Minkowski diagram is a combination of two coordinate systems.
Take a line from the event parallel to the space axis of observer 2. The adjustable region selection bar is shown as a dotted outline in each frame. Feedback on the Sequence Diagram Tutorial.
If you have any suggestions or questions regarding the sequence diagram tutorial feel free to leave a comment. The Knox index the Mantel index the Spatial-temporal moving aver age and Correlated Walk Ana lysis. Using a Template Cube value allows you to use a consistent spatial extent and Time Step Interval value while analyzing different datasets.
The concept of space time diagram in pipelining is explained in this videoif you like the video then do sharethank you. A speci c point on a space-time diagram is called an event To make a space-time diagram take many snapshots of the objects over time and set them on top of each other. Now we want to show that the measurement of time intervals in the S frame are not the same as those in the S0frame using Minkowski diagrams.
The space-time diagram on the right shows the same events from the point of view of an observer initially moving with one of the moving quints. The default is days. A point on the spacetime diagram is called an event.
Building a visual space-time diagram from individual frames of video. In such a diagram light rays always follow paths with a. Below the animation is a more detailed tutorial and some examples and excercises.
Supernova spreads out in both directions along the trajectories shown. Another dot for event 2 because x 2x 1. The horizontal value event is the position of the event as measured by observer 1.
However for rectilinear or planar motion we can depict a particles movement. Construct a world line of the particle that is resting at 2 m from the reference event. Figur e 91 shows the Space-Time Ana lysis screen.
The vertical value of this event is the time as measured by observer 1. Each such observer labels events in space-time by four inertial. This is a point in space at a speci c moment in time.
Minkowski space time diagram Minkowski space time diagram. Ct x x 45º 45º 12 v c v ct2 ct1 ct T142 Thect9- and x9-axes drawn on our ct-xspacetime diagram. 28 Spacetime Diagrams Note.
Business Process Modeling Tutorial BPM Guide Explaining Features. This sequence diagram tutorial covers everything you need to know on sequence diagrams and drawing them. The two events may also be shown in real time by pressing the buttons Play worldline t or Play worldline t.
Lines in the diagram are like contrails through time. An event is anything that can be characterized by a single point on a spacetime diagram or on a position vs time graph. On the space-time diagram.
In a Flatland Minkowski Diagram there are two axes for space a plane and one axis for time. Assume that the planet is not moving relative to the star. Space-time diagram for cart collision in laboratory reference frame assimilated from 120 video frames.
Please see the diagram below. The Enterprise will fly by at a constant velocity past the planet and beam up the students without stopping. We do so with a spacetime diagram in which spatial axes one or two are drawn as horizontal axes and time is represented by a vertical axis.
One division of the space axis corresponds to 1 meter. Creating an actual space-time diagram from stacked strips of video frames. A space-time diagram shows the history of objects moving through space usually in just one dimension.
T141 A spacetime diagram showing worldlines of three light pulses and three particles. The left-hand section of the figure shows the Galilean transformation into. Computation of each step within the sample time ie.
We cannot as creatures stuck in 3 physical dimensions draw the full 4 dimensions of spacetime. In the jargon of spacetime diagrams the green point on Toms and Sarahs plots is an event and the red or blue trajectories are worldlines. A spacetime diagram is nothing more than that but for historical reasons the axes are reversed so that position is on the horizontal axis and time is on the vertical axis.
Crim eStat includes four space-time techniques. This sequence diagram tutorial covers everything you need to know on sequence diagrams and drawing them. As already explained in our introduction the special theory of relativity describes the relationship between physical observations made by different inertial or nonaccelarating observers in the absence of gravity.
Which events occur at the same place. Particles 1 and 2 leave x 0 at t 0 accelerating from rest in opposite directions. Real-time control timing If the sample time of our program is T you can see that the program is executed at distinct points in.
Thus in the situation shown in 3 space-time diagrams below the central section shows the worldline of one stationary observer one observer moving to the right and two events on the future light cone on the event where the two observers worldlines cross. An event must have both a time and a place and. For example you might use last years space-time cube as a template cube once the next years data is acquired as this ensures consistency in both the spatial extent and the Time Step Interval value being used while allowing the cube to extend to.
The two events will then appear in space and time given time unit 1 second. Hence a Flatland Minkowski Diagram is a 3-Space with light cones as in the diagram below. Before the next step starts.
The space-time diagram above shows particles with different velocities. Answer the following questions. In a Flatland Minkowski Diagram there are two axes for space a plane and one axis for time.
Because the speed of light is special in relativity space-time diagrams are often drawn in units of seconds and light-seconds or years and light-years so a unit slope 45 degree angle corresponds to. The Lorentz transform is then just a way of changing those diagrams from one frame to another. Meas urement of Time i n C rime Stat Time can be defined as hours days weeks months or years.
An event a particular place at a particular time is represented by a point on the Minkowski Diagram. Notice the two sets of equal angles. One in which an observer is at rest relative to certain events and another for an observer in relative motion to the first.
Diagram for showing time dilation for events located at a fixed point in frame S.
A 3 Spacetime Diagrams Ibdp Physics

The Basics Of Spacetime Diagrams Youtube

Spacetime Diagrams Special Relativity Ch 2 Youtube
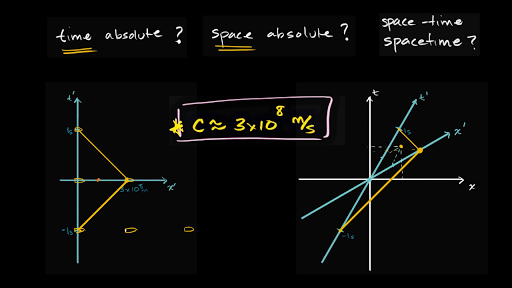
Introduction To Special Relativity And Minkowski Spacetime Diagrams Video Khan Academy



0 comments
Post a Comment